 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26

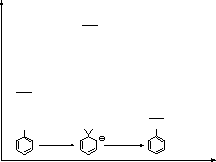
![]() Mechanism
Mechanism
and/or para position in order to operate
it is typically a replacement of a halide with a nucleophile
![]() Free
Free
![]() Energy
Energy
increase the rate of reaction. Electron donating groups retard the rate of reaction.
![]() enable stabilisation of charge.
enable stabilisation of charge.
intermediates. The rate is not determined by leaving group ability but rather the ability
to form Meisenheimer complex.
![]() 2
2![]() orbitals form a π bond orthogonal to the plane of the
orbitals form a π bond orthogonal to the plane of the
aromatic π cloud.
![]() 2N
2N
![]() 2
2
![]() 2N
2N
![]() 2
2
![]() picric acid
picric acid
![]() 2
2
![]() 4500 lb/in
4500 lb/in![]() 2
2
![]() 2O, warm
2O, warm
![]() X-
X-