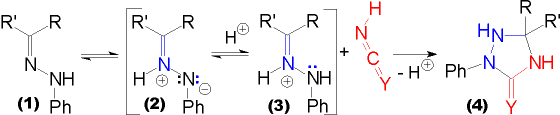
| The formation of triazolidin(thi)ones (4, Y = O / (S)) using potassium (thio)cyanate can be envisaged as a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of (thio)cyanic acid (being the dipolarophile) to the hydrazone (1). In similar cyloaddition reactions involving hydrazones in acidic media, the active species is assumed to be the prototropic |
azomethine imine, a 1,3-dipole (2), or the N-protonated hydrazone (3). The possibility of such "prototropic" pathways leading to 1,3- and 1,5-dipoles and their application in cycloaddition reactions involving such isomers has been discussed in a more general view by Grigg1. |