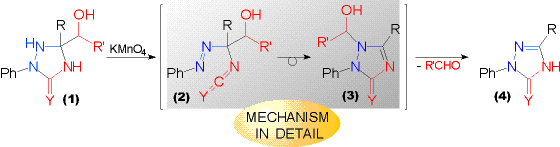

| Upon oxidation with potassium permanganate the hydroxyalkyl substituted triazolidinones (1, Y = O) and -thiones (1, Y = S) yield the triazolinones (4) directly with unsubstituted ring position 1, i.e. under formal loss of the former hydroxyalkyl substituent as a carbonyl compound. Presumably the substituent is split off as a carbonyl compound. | This is supported by the isolated oxidation product from the OXIDATION OF THE HYDROXY - CYCLOHEXANONE DERIVED TRIAZOLIDINONE. Mechanistically, several conceivable REACTION PATHWAYS may be considered accounting for the products formed. |
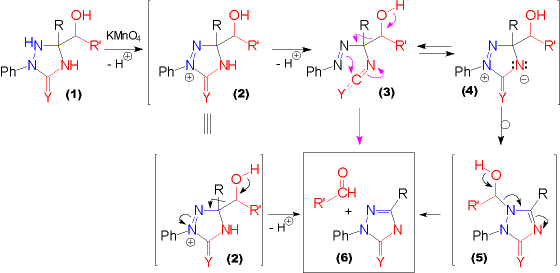
| There are several possible reaction pathways that can account for the products obtained in this oxidation reaction. Some rearrangement and fragmentation processes are outlined in this scheme. It is assumed, that the first step in this oxidation is the abstraction of a hydrid ion from the nitrogen atom in ring position 1 of the triazolidin-3-one (1, Y = O) or -3-thione (1, Y = S) by the oxidant. The first of these optional pathways shows deprotonation and a Grob type fragmentation of the oxidized species (2) to form the according triazolinone (6) and the carbonyl compound directly. | The alternative pathways require further abstraction of a proton from the compound (2) to give rise to the isocyanates (3, Y = O) or isothiocyanates (3, Y = S). From this point again two paths are open. The first one forms the products via a Grob type fragmentation, the other one involves the valence tautomeric equilibrium with a zwitterionic species (4) which rearranges to the according triazolinone (5). This hemiaminal eliminates the former hydroxyalkyl substituent as a carbonyl compound to form (6). |
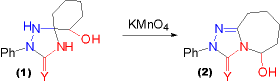
| In the case of the hydroxycyclohexanone derived triazolidinone (1) evidence was found that the former hydroxyalkyl substituent is split off as a carbonyl compound. In the oxidation of the spiro triazolidinone (1) the carbonyl moiety generated in the course of the reaction is tethered to the triazolinone | and forms a stable intramolecular hemiaminal (2). The position of ring fusion (ring position 4 rather than position 1) is not indicative of any suggested reaction pathway (compare different possible REACTION PATHWAYS FOR THIS TYPE OF OXIDATION), since there may be equilibration of hemiaminals after the reaction proper. |
| TOPICS OF: | E) OXIDATION HYDROXALKYLTRIAZOLIDINONES: |
| E1) General Reactivity E1.1) Reaction Pathways E1.2) Oxidation of Spirotriazolidinone NEXT chapter HOME INDEX |