 |
This is a first year course given by Dr David Widdowson. The notes were written by Matthew Parkinson and edited to match the CREDIT format by Ross Walker. |
 |
This is a first year course given by Dr David Widdowson. The notes were written by Matthew Parkinson and edited to match the CREDIT format by Ross Walker. |
1. Introduction
1.1 Scope
1.2 Coverage
1.3 Course Objectives2. Nitro Alkanes and Nitro Arenes
2.1 Structure
2.2 Electronic Effects
2.3 Spectroscopy
2.4 Synthesis of Nitro Compounds2.4.1 Gas Phase Nitration of Alkanes2.5 Reactions
2.4.2 Electrophilic Nitration of Anions
2.4.3 Nitrate SN2 Displacement of Alkyl Halides
2.4.4 Oxidation with Peracids
2.4.5 Aromatic Nitro Compounds2.5.1 a Anions2.6 Summary
2.5.2 Alkylation2.5.2.1 Henry Reaction2.5.3 Reduction
2.5.2.2 Michael Additions
2.5.2.3 Ambident Nucleophiles2.5.3.1 General
2.5.3.2 Photochemically
2.5.3.3 Metal/H+ Reaction
2.5.3.4 H2/Pd Surface Reactions
2.5.3.5 Sulphur Reagents
2.5.3.6 Metal Hydrides3. Nitroso Compounds
3.1 Structure
3.2 Electronic Effects
3.3 Spectroscopy
3.4 Synthesis3.4.1 Aromatics
3.4.2 Aliphatics
3.4.3 Tertiary Aliphatics3.5 Reactions3.5.1 Addition and Condensation
3.5.2 Reduction
3.5.3 Oxidation
3.5.4 Radical Addition-Spin Trapping3.6 Summary4. Amines
4.1 Nomenclature
4.2 Structure
4.3 Electronic Effects
4.4 Spectroscopy
4.5 Physiological Effects
4.6 Synthesis4.6.1 Alkylation Reactions3.6.1.1 General4.6.2 Reductive Methods
3.6.1.2 Alkylation of Phthalimide Anion-The Gabriel Synthesis
3.6.1.3 Alkylation of Bis(Phenylthio)Amine Anion
3.6.1.4 Alkylation of Trifluoromethanesulfonylamine3.6.2.1 Reduction of Amides4.6.3 Hydrolytic Methods
3.6.2.2 Reduction of Nitro Compounds or Azides
3.6.2.3 Reduction of CN Multiple Bonded Systems
3.6.2.4 Eschweiler-Clarke Synthesis3.6.3.1 Hydrolysis of Amides4.6.4 Rearrangements
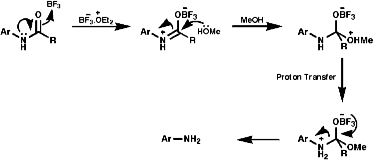
3.6.3.2 MeOH/BF3.Et2O
3.6.3.3 Meerwein's Salt3.6.4.1 General Reaction Scheme
3.6.4.2 Hoffmann Rearrangement
3.6.4.3 Curtis Rearrangement
3.6.4.4 Lössen Rearrangement
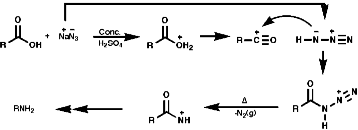
3.6.4.5 Schmidt Reaction
3.6.4.6 Beckmann Rearrangement
3.6.4.7 Abnormal Beckmann Rearrangement4.7 Reactions4.7.1 Basicity and Nucleophilicity
4.7.2 Alkylation
4.7.3 Acylation
4.7.4 Halogenation4.7.4.1 Aliphatics
4.7.4.2 Aromatics4.7.5 Nitrosation4.7.5.1 General
4.7.5.2 Primary Amines
4.7.5.3 Secondary Amines
4.7.5.4 Tertiary Amines4.7.6 Reaction with Carbonyls
4.7.7 Oxidation4.7.7.1 Oxygen Addition Reactions
4.7.7.2 Dehydrogenation of Amines4.7.8 Deprotonation4.8 Summary5. a Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
5.1 Amino Acid Nomenclature
5.2 Amino Acid Structure
5.3 Amino Acid Synthesis5.3.1 The Gabriel Synthesis
5.3.2 The Streaker Synthesis
5.3.3 Enantioselective Synthesis5.4 Peptide and Protein Structure
5.5 Peptide Synthesis5.5.1 General
5.5.2 Merrifield Solid Phase Synthesis
5.5.3 Peptide Synthesis in Nature5.6 Summary
6. Nitrogenous Natural Products and Alkaloid Biosynthesis
6.1 Introduction
6.1.1 Amino-acids, Peptides, Proteins and Derived Substances
6.1.2 Vitamins
6.1.3 Porphyrins, Chlorins and Cobalamins
6.1.4 Purines, Pyrimidines, Nucleosides, Nucleotides6.2 Alkaloid Biosynthesis
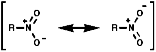
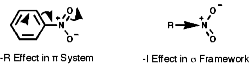
Due to the -I inductive effect of the s bond the pKa values of nitro group containing compounds can also be affected;
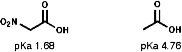
Ph-NO2, this substituent is ortho, para directing due to the -R resonance effect of the p bond. The -I will also still operate but is less obvious here.
NMR
For a CH protons, adjacent to the group, the chemical shift, d, = 4.3,
due to electron withdrawing effect;
![]()
U.V .
The nitro group causes a pronounced shift of lmax to longer
wavelengths when conjugated to unsaturated p systems, a bathochromic shift.
This is why nitro compounds are often yellow.
Gas Phase Nitration of Alkanes
This commercial free radical process involves the NO2 radical;
![]()
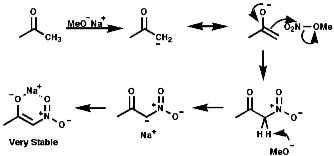
Electrophilic Nitration of Enolate Anions
The use of the enolate active methylenes forms a stable product due
to the chelation of the counter ion;
Nitrate SN2 displacement of alkyl halides
![]()
Two products, a nitro compound and a nitrite ester, are produced due to the sodium nitrate acting as an ambident nucleophile, either a N or O nucleophile;
![]()
The use of silver nitrate produces only the nitro compound as it is not an ambident nucleophile.
Oxidation with Peracids
Nitro compounds can be produced by oxidised of amine by peracids;
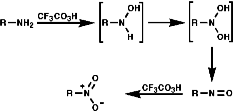
Aromatic Nitro Compounds
These are synthesised by electrophilic aromatic substitution with NO2+
ions;
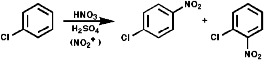
a Anions
a anions are easily formed with base and stabilised by resonance as
nitronate anions, c.f. C=O enolate formation;
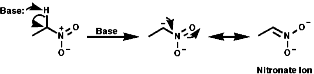
The protons on nitro methane, MeNO2, have a pKa of 10.2, c.f. MeCOCH2CO2Et pKa 11. So in order to remove the a protons on nitro alkane an appropriate base in required.
As the nitronate ion is delocalised it is a soft nucleophile and show usual reactivities of stabilised, soft, carbanions.
Alkylation
![]()
Henry Reaction
This reaction is analogous to the Aldol reaction;
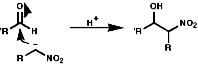
If R' is aryl the mechanism of elimination is;

If R' is alkyl the mechanism of elimination is;
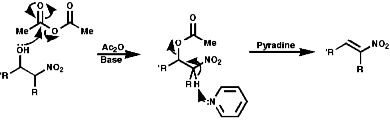
Michael Additions
The Michael addition is a conjugate addition as the double bond is
the soft centre of the ester, the carbonyl carbon being the hard centre.
It proceeds by the following mechanism;
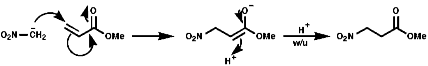
Ambident Nucleophiles
Nitronate anions themselves can act as ambident nucleophiles
with either attack from the C, a soft nucleophile, or from the O,
hard nucleophile. These will attack soft or hard electrophiles respectively;
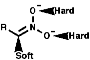
This ambident behaviour can be seen in the Nef reaction;
O-alkylation is Possible with a hard alkylating agent like Meerwen's Bact, this is a Me+ source;
![]()
The ambident nature of the nitro group makes it a very versatile reagent.
Reduction
General
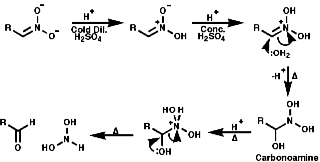
In principle the reduction of nitro compounds should follow the path;
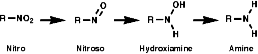
The reduction of nitroso groups is generally more easily achieved but the nitro group can be reduced in a number of different ways;
Photochemically
![]()
Metal/H+ Reactions
Metals, such as Fe, Zn, Sn can be used with H+ to reduce
the nitro group by a sequence of single electron transfer (SET)/protonation
reactions;
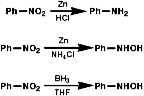
The mechanism for the Zn/H+ reaction is;
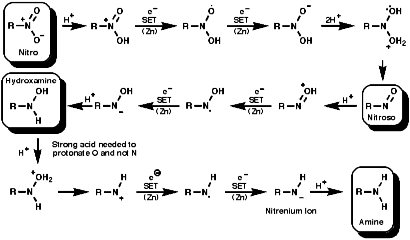
H2/Pd Surface
Reactions H2/Pd or Pt can be used by heterogeneous
H- transfer on the metal surface and then reaction with the
nitro compound;
![]()
Sulphur Reagents
NaSH or Na2Sx or (NH4)2S2
can be used and possibly precede by SET reactions;
![]()
Metal hydrides
Reagents like LiAIH4, but not usually NaBH4,
reduce the nitro group by hydride, H-, transfer. The product
will depend on the nature of the reducing agent, but the end point is ultimately
an amine.
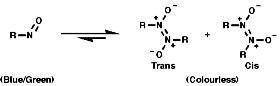
NMR
For a CH protons, adjacent to the group, the chemical shift, d, = 4.0,
due to electron withdrawing effect.
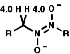
![]()
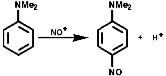
They can also be produced from nitro compounds by reduction to the hydroxylamine then followed by oxidation;
![]()
The nitroso compound comes out of aqueous solution, due to its non hydrophilic nature, and so avoids further oxidation, this is a very general method and can be used for a verity of compounds. The direct reduction from NO2-R to NO-R is not a generally feasible process though a photochemical method is known, see nitro group section.
Aliphatics
The synthesis of aliphatic nitroso compounds can achieved by nitrosation
of active, acidic, methylene compounds under acidic conditions, H+/NOCl,
N2O3 or N2O4;
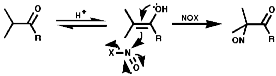
Under basic conditions, C5H11ONO/NaOEt;
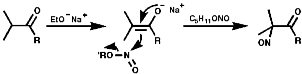
Under neutral conditions enol silyl ether /NOCl;
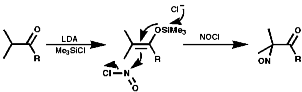
Another method of synthesis is by Markovnikov addition of NOX (X=Cl, NO2, NO3) to olefins.
Tertiary Aliphatics
To synthesis nitroso compounds with tertiary alkyls another method
has to be employed;
![]()
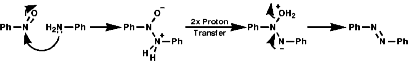
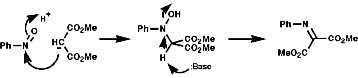
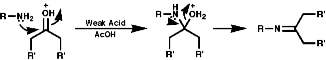
The best method for preparation of secondary hydroxylamines is by addition of a Grignard reagent to a nitroso group and carrying out an acidic work up;
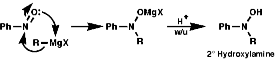
The production of a nitrone can be seen in the following reaction;
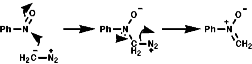
The hetero Diels-Alder reaction is also possible;
![]()
Reduction
Reduction occurs as for NO2 groups with metals, metal
hydrides, hydrogen/ catalyst.
![]()
Oxidation
Oxidation is readily brought about with peracids inter alia, this is
not possible for nitro groups.
![]()
Radical Addition-Spin Trapping
Monomeric nitroso compounds are used to detect transient free radicals,
mainly carbon centred radicals, by 'trapping' them as stable nitroxide
radicals. These can be detected and assayed in an EPR spectrometer, this
is the electron equivalent of the NMR spectrometer. EPR stands for Electron
Paramagnetic Resonance. This allows the intermediacy of such otherwise
undetectable transients to be proven and is therefore a valuable mechanistic
probe.
If the following thermal decomposition of benzoyl peroxide, a radical initiation reaction, is to be monitored;
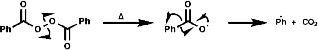
The phenyl radical would be undetectable by EPR but by addition of a tertiary nitrosyl the more stable nitroxide is produced which is observable;
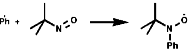
![]()
The fact this rate of inversion is so regular is exploited in the ammonia clock. An important implication of this is that chiral amines racemise rapidly. This can be stopped by use of a rigid framework, an example of which is 1-aza-bicyclo-[2,2,2]-heptane;
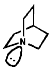
![]()
NMR
For protons in the a position to a primary amine, e.g -CHNH2,
the protons have a chemical shift of d 2.5-3. Protons in the a position
to a tertiary amine, e.g CH3NR2, have a chemical
shift of d 2.0-2.5. Protons in the a position to a quaternary ammonium
ion, e.g -CHN+R3, have a chemical shift of d 3.5
- 4.0.
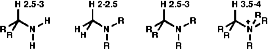
Alkylation Reactions
The synthesis of primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary amines
involving direct alkylation of ammonia and lower amines. The reaction proceeds
with nucleophilic attack by the loan pair on nitrogen and then abstraction
of the extra proton with a base that is more nucleophilic than the amine.
It is not generally an efficient process because of ready over reaction;
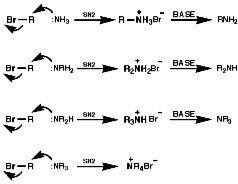
Other leaving groups that can be exploited in direct alkylation are;
Due to the problem of over alkylation more specific methods have been developed;
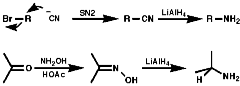
Alkylation of Phthalimide Anion-The Gabriel Synthesis
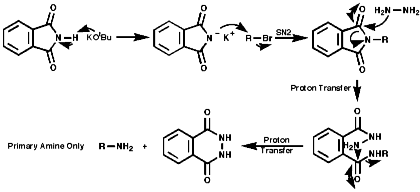
Hydrazionlysis of the product releases the primary amine.
Alkylation of Bis(Phenylthio)Amine Anion, (PhS)2N-
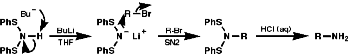
Acid cleavage again gives the primary amine.
Alkylation of Trifluoromethanesulfonylamine Anion, RN-SO2CF3
Cleavage with LiAlH4, or base, gives the secondary amine.
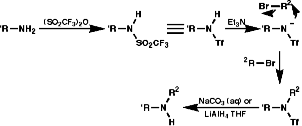
Reductive Methods
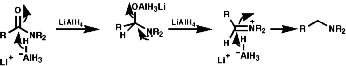
This method is best for tertiary Amides but is also OK to use for secondary and primary amines with the use of BH3.THF as this reagent is a little more delicate than LiAlH4! This method also gives an unambiguous synthesis of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
![]()
This reaction requires acidic conditions to produce the protonated form of the first product. This means that a mild hydride, H-, source is required an example of this is HCO2H/HCO2-Na+;
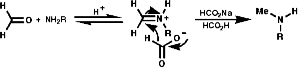
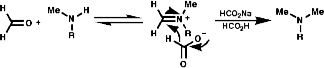
It is also possible to use NaBH3CN which is acid stable at pH 4.Hydrolytic Methods
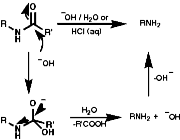
For hindered or sensitive systems it is inefficient or impossible. Special methods for these transformations include;
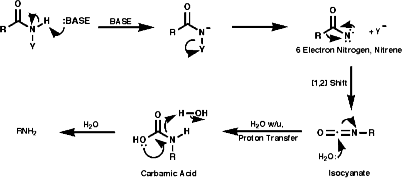
Theses reactions are a convenient source of many amines from carboxylic acids, with the loss of the carboxyl carbon atom, or ketones, with the loss of one of the groups on the carbonyl carbon. Example of such rearrangements are;
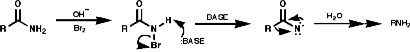
![]()
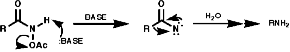
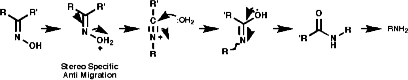
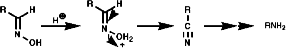
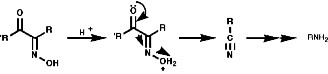
Amine |
pKa |
| NH3 |
|
| EtNH2 |
|
| Et2NH |
|
| Et3N |
|
| PhNH2 |
|
| PhNEt2 |
|
![]()
In general nucleophilicity parallels basicity except for increase of stability due to steric hindrance.
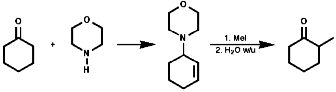
Alkylation
This has been largely discussed under synthesis. One important area
is the alkylation of aryl amines which N-alkylate;
![]()
Quaternary salts undergo the mechanistically important Hoffmann elimination reaction. In this, the pyrolysis of quaternary ammonium hydroxides produces the less substituted, less thermodynamically stable, olefin, in contrast to the more common Saytzeff elimination which produces the more substituted more thermodynamically stable, olefin;
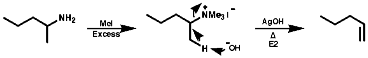
This indicative of a kinetically controlled reaction, and so is reversible, with an early transition state. Consider the reaction profile;
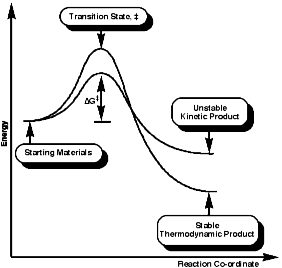
It can be seen that the activation energy, DGý, for the Hoffmann product is lower than for the normal thermodynamic product, this implies that the process is controlled by the proton removal step;
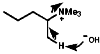
As the C-H bond gets weaker, CH3>CH2>CH, the proton becomes more acidic so under these circumstances the more acidic methyl group proton will be preferentially removed, this results in the less substituted olefin, and the stability of the product is irrelevant to the process. The stereochemistry of the reaction is trans coplanar;
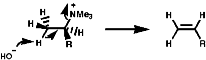
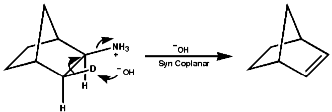
Syn coplanar reactions are known when a trans array is geometrically prohibited, this is seen in some caged ring systems like bicyclo-[2,2,1]-heptane;
Acylation
Acylation of primary and secondary amines with RCOX where X is a good leaving group like a halogen, OCOR' or OR group. It is a very common process, occurring via the tetrahedral addition product of the active carbonyl group;
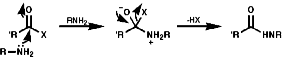
Halogenation
Aliphatics
N-Halo,Cl, Br, I, compounds are readily formed with Hal+
reagents;
![]()
![]()
These N-Hal species are not very stable and readily eliminate HX to give imines (RCH=NR') especially on treatment with bases like NaOEt. Hydrolysis of the imines generates carbonyl groups and the overall process represents a reversal of the Eshweiler-Clark reaction;
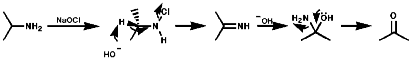
![]()
Aromatics
In benzene rings carbon attack of Hal+ is very common and
has been dealt with before in the course. The amino group is electron releasing
and o, p directing;
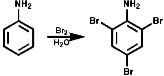
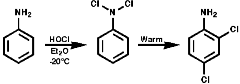
At low temperatures, ² -20°C, N-chlorination is often observed. The mono- or di- N-chloroamines rearrange rapidly on warming to the 2-, or 4-, or 2,4-di-chloroamines;
Nitrosation
Nitrosation, with the active agent of NO+ from HNO, NOCl,
N2O3, N2O4, is not subject
to any significant steric inhibition, due to the small size of the NO+
group, and any nitrogen with a nucleophilic lone pair of electrons will
react. The products depend on the nature of the amino function.

They undergo nucleophilic attack by secondary amines at the terminal nitrogen to give the carcinogenic triazenes ArN=NNR2. Many other nucleophiles will react analogously;
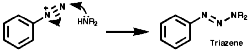
Fragmentation of the aryl diazonium ions can occur by ionic or single electron transfer, SET, radical mechanisms dependent upon the conditions. The copper (I) catalysed reactions, Sandmeyer reactions etc, proceed by the SET mechanism which generates the aryl radicals;
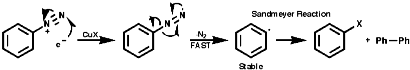
Thermal decomposition or reactions with simple nucleophiles are more likely to proceed via the ionic fragmentation to the highly reactive aryl cations;
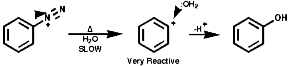
In either case, the overall product is the replacement of the N2+ group with a nucleophile, Hal-, CN-, OH- etc.Aliphatic diazonium ions are not stabilised and undergo very rapid fragmentation to N2 and an alkyl cation;
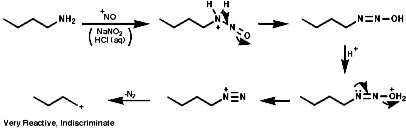
This species is itself very reactive and therefore indiscriminate in is reactions with nucleophiles. A plethora of products, including those resulting from rearrangement of the initially formed carbocation, are usually observed;
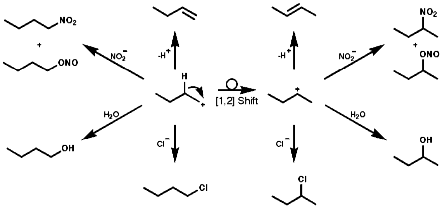
![]()
The N-nitrosoarylamines readily rearrange on treatment with acid to the para substituted products, the FIcher-Hepp rearrangement;
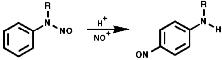
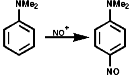
In the aliphatic series, the initial N-nitrosation, to form R3N+-NO, is readily reversible but upon warning the product fragments to a secondary N-nitrosamine, R2NNO, and an aldehyde, RCHO;
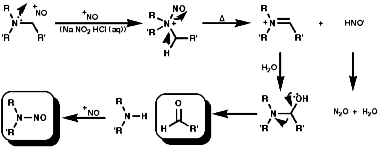
If R is aryl, Schiff's bases, then conjugation makes them stable;
![]()
If R is aliphatic there is no possibility of conjugation and so they polymerise and are not generally isolable;
Secondary amines condense to form enamines, R2NCR=CR2;
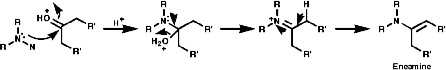
Enamines are important synthetic intermediates which will be covered in the 2nd year course, they readily undergo electrophilic attack at the b carbon;
Tertiary amines simply act as bases.
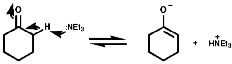
Oxidation
![]()
Secondary amines are similarly oxidised to the hydroxylamines, R2NOH.
![]()
Tertiary amines are readily oxidised by many peracids to the amine oxide, R3N+-O-;
![]()
These are useful for their fragmentation on pyrolysis, the Cope elimination reaction;
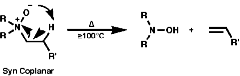
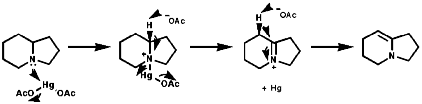
![]()
The pKa's of amines are typically NH3=34, Et2NH=36 and iPr2NH=38; i.e. R2N- are strong bases and they are very much used for this purpose in base catalysed reactions. The deprotonation of hindered amines, with bulky R groups, makes for a very strong base which is a very weak nucleophile. Commonly used examples are;
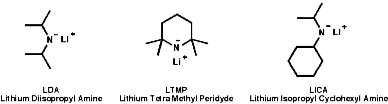
The use of these bases can be useful in synthesis for deprotonation of activated C-H bonds, those adjacent to electron withdrawing groups;
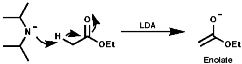
R |
Name |
R |
Name |
|
| -Me |
|
-CHMe3 |
|
|
| -CH2CHMe2 |
|
-CHMeCH2Me |
|
|
| -CH2Ph |
|
-CH2C6H4OH |
|
|
| -CH2OH |
|
-CHMeOH |
|
|
| -CH2CO2H |
|
-CH2CONH2 |
|
|
| -CH2CH2CO2H |
|
- CH2CH2CONH2 |
|
Their general structure is chiral when R is not another CO2-, NH3+ or H, therefore glycene, R=H, is achiral;

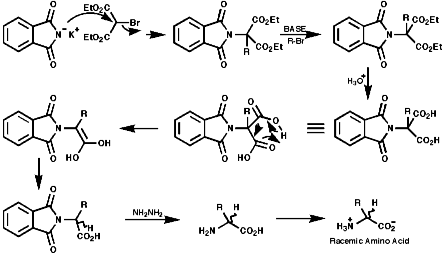
The Gabriel Synthesis
The can be readily adapted for amino acids;
The Streaker Synthesis
This is a direct approach, but not enantioselective;
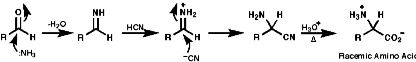
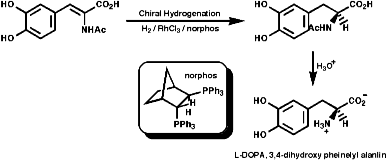
Enantioselective Synthesis
This modern method of making only one stereo isomer include the asymmetric
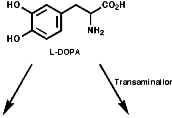
hydrogenation of dehydroamino acid derivatives. For example the Monsanto
synthesis of L-DOPA;
Peptide and Protein Structure
These are oligomers, peptides, and polymers, proteins, of the a amino
acids, linked via amide or 'peptide' bonds;
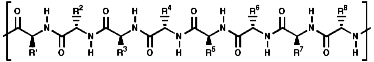
Thus a tetra peptide would be;
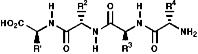
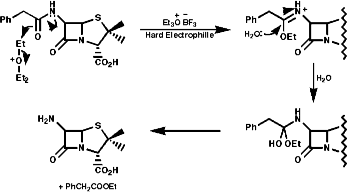
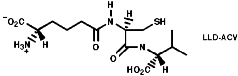
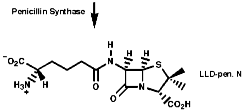
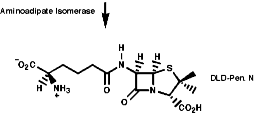
Many hormones like oxytocin or antibiotics like penicillin and cephalosporin are peptides, sometimes with modification of the backbone chain, this can be seen in penicillin N;
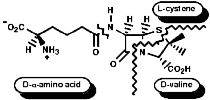
Penicillin is biosynthesised from the individual amino-acids by an unusual pathway unravelled very largely by the Oxford group lead by Professor Jack Baldwin. The sequence is;
![]()
This will be looked at in more depth later.
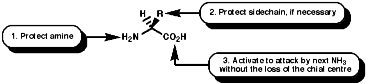
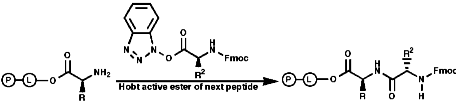
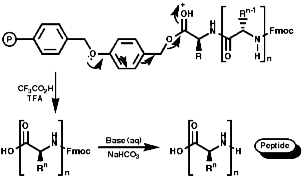
Peptide synthesis can be carried out in homogeneous solution but due to the non 100% yield nature of all the protection steps a low yield of the final peptide is found. To get around this problem frequently the Nobel prize winning Merrifield solid phase synthesis is now used. This process uses excess reagents to drive each reaction to 100% yield and so can be used to synthesise peptides of 10-20 units, of any sequence, in good yield. The process can be automated and peptides can be made very quickly.
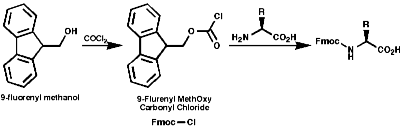
Merrifield Solid Phase Synthesis
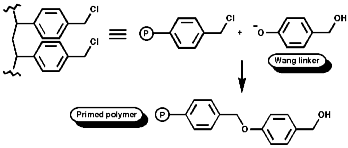
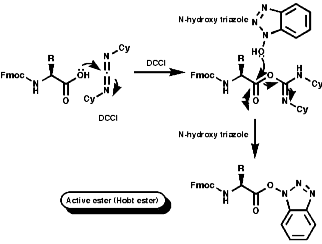
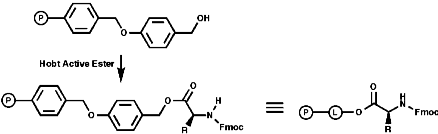
The general principles of this method can be expressed as;
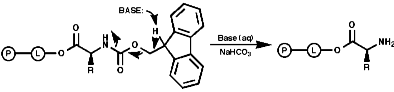
The coenzyme B12, Co2+ or 3+, for certain liver functions in animals;
Chlorophyll, Mg2+, for photosynthesis in plants;
For further information see Vollhardt chapter 25.
The basic reaction set, the ready interconversion in vivo of carbonyl groups, imines, enamines, and their derivatives, is;
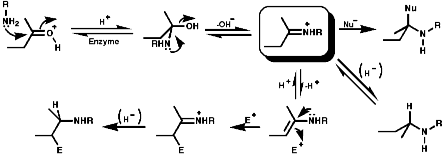
1-Benzyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-isoquinolines are subject to enzymic 'phenol oxidative coupling' in which the one electron oxidant is usually a copper containing enzyme. The process well illustrated by the chemical oxidation of p-cresol with potassium hexacyanoferrate;
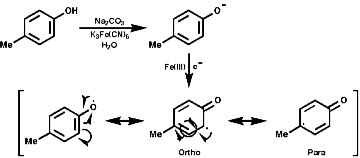
Radical coupling between the para and ortho cononical dominates producing Pummer's ketone;
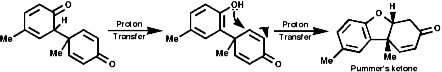
This is the basis for the formulation of the opium alkaloids. The overall sequence is;
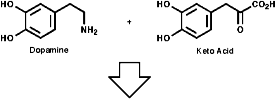
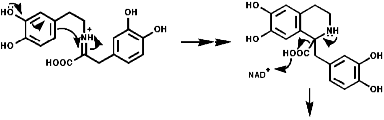
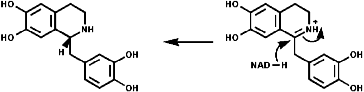
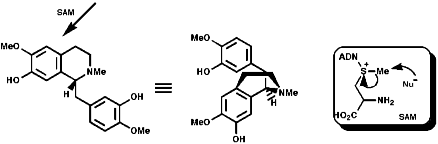
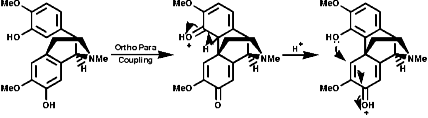
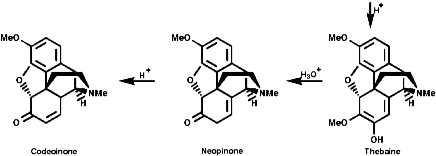
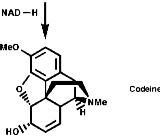
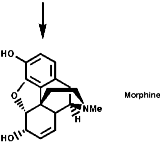
The sections on biosynthesis are intended to link with 'real' organic
chemistry and to link with the polyfunctional and mechanistic chemistry
presented in second year. They are for interest only and not for examination.
purposes.