|
Why there is a need for a more effective influenza treatment |
|
Comparison of the symptoms of the 'flu with that of a common cold |
| Relenza
(Zanamivir for oral
inhalation) is the first in a new generation of influenza virus-specific drugs
known as neuraminidase inhibitors, which work by interferring with the
life cycles of influenza viruses A and B. It prevents the virus
spreading infection to other cells by blocking the neuraminidase
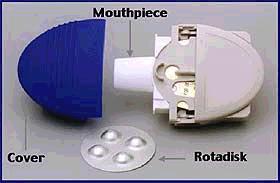
enzyme present on the surface of the virus. Relenza is available as a powder
that is administered by inhalation of 2 blisters from the rotadisk inside
the diskhaler (Fig. 1) twice daily for five days. This
means that 20mg of Relenza is delivered to
the principal site of viral replication each day.
The main method for preventing influenza since the 1960s is by vaccination and although this and anti-viral drugs such as amantadine and its analogue rimantadine have long been available (since 1976 and 1993 respectively), they are only of limited use because of the constant mutation of the virus. This chameleon-like nature also means that the virus can become unrecognizable to the human immune system and thus repeatedly infect millions of people year after year. |
|
|
Comparison of the
symptoms of the 'flu with that of a common cold:
|
| Influenza | Cold |
| Sore throat | Mild sore throat |
| High fever and chills | Low-grade fever |
| Non-productive cough | Cough |
| Severe muscle aches | Congestion |
| Headache | |
| Intense fatigue. |
| The effect of Relenza on
patients with respiratory diseases:
Relenza is not generally recommended for the treatment of patients with respiratory dieseases such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and has carried an approval since its approval in July 1999. Some patients with underlying airway diseases have experienced serious adverse events following treatment, with some fatal outcomes although causality has been difficult to establish. It has been recommended that patients with asthma have a fast-acting bronchodilator inhaler available and use it about 15 minutes before taking Relenza.
|
| Successfulness
of Relenza:
The sialidase inhibitory activities (determined by methods described in reference 7) of Relenza compared to the more recent neuraminidase inhibitor Oseltamivir are shown in the table below9. IC50 is the concentration that reduces enzyme activity by 50%.
The results demonstrate that both compounds are good inhibitors of influenza A and B, with Oseltamivir being more selective towards Influenza A and Relenza showing a better overall performance. In phase I and II tests reported by the Lancet5, no important adverse effects were found in healthy patients or those reported to have mild to moderate asthma following an inhaled administration of 40mg/day of Relenza. There was a significant improvement of the symptoms of people taking Relenza compared to those taking the placebo.. |
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||