| Total energies (kcal/mol) based on AM1 calculations | ||
|---|---|---|
| A: 245.2 | B: 138.1 (=383.3) | C: 330.8 |
| D: 262.5 | D: 281.2 | E: 217.1 |
| E: 216.2 | F: 221.9 (Huckel) | F: 230.4 (Mobius) |
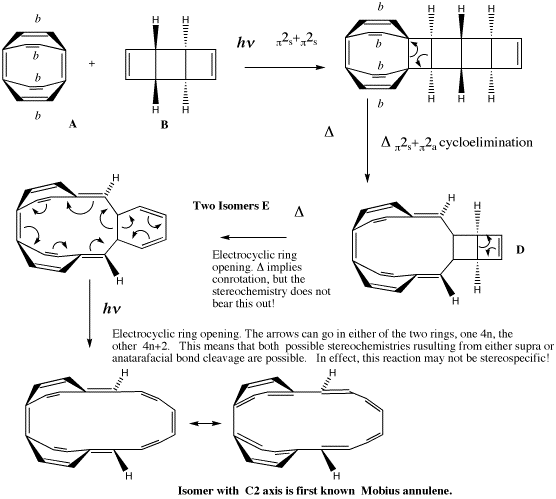
| Electrocyclic TS, 4n+2 Electrons, a plane of symmetry Energy (B3LYP/6-31G*) -464.3514, Huckel aromaticity in 6-ring NICS(0) -11.1/+0.3 for 6/8 ring (Benzene = -10) | Electrocyclic TS, 4n Electrons, an axis of symmetry
Energy -464.3718 (-12.8 kcal), Mobius aromaticity in 8-ring. NICS(0) +2.5/-9.5 for 6/8 ring (Benzene = -10) |
|---|---|
| Electrocyclic TS, 4n+2 Electrons, a plane of symmetry Energy (B3LYP/6-31G*) -309.5374, Huckel aromaticity in 6-ring NICS(0) -12.4/+0.2 for 6/4 ring (Benzene = -10) | Electrocyclic TS, 4n Electrons (but the axis of symmetry is only approx)
Energy -309.4782 (+41.8 kcal) Mobius aromaticity in 4-ring. NICS(0) for +0.4/-5.1 6/4 ring (Benzene = -10) |
| Question 2a: For models of the norbornyl cation, see earlier tutorial | ||
|---|---|---|
| Question 2b Initial carbocation: 238.9 kcal/mol | First WM shift: 219.0 | |
| Second WM shift: 201.3 kcal/mol | Third WM shift: 182.3 | |
| Fourth WM shift: 163.5 kcal/mol | Fifth WM shift: 143.6 | |
| Question 2b product | Question 2c. Eschenmoser fragmentation using MeO as a model for TsO. |
|
| Question 2c. Proton removed to form anion | Epoxide opened. Note linear conjugation of chain. | |
| B3LYP/6-311+G(3d) Transition state for Eschenmoser elimination. -794.7344/-794.7326 | ||