
Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)
|
| Poly(lactic acid), a biocompatible and biodegradable material, is rapidly gaining in importance as an environmentally sustainable alternative to petrochemical-derived products. It finds a wide range of uses, from biomedical implantation devices, e.g. sutures, rods, plates and pins, through artificial skin and drug delivery agents to environmentally benign film and fibres for packaging and clothing. |
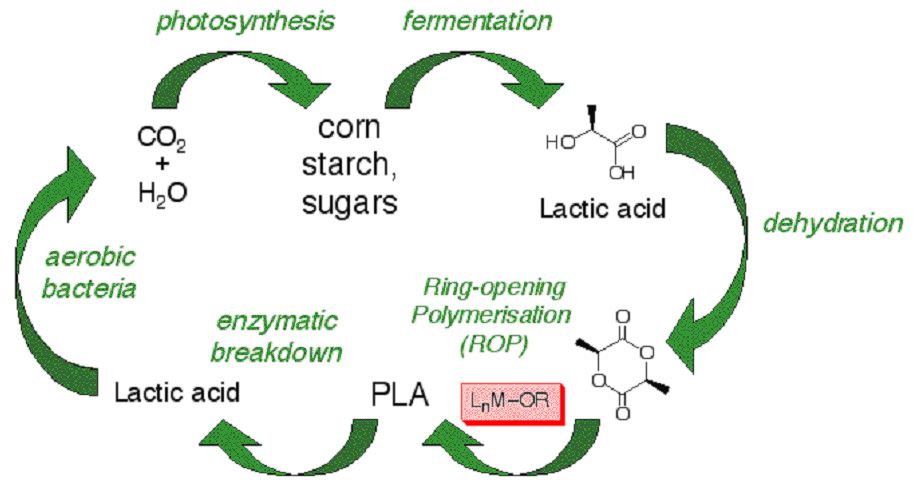
In recent work, we have described new tin(II) and iron(II) based initiators supported by beta-diketiminate ligands. These complexes initiate the living polymerisation of lactide under mild conditions.
|
|
|