Condensation Polymerisation
A chemical reaction where two reactants combine to form a polymer with the expulsion of a small molecule is called condensation polymerisation. This type of reaction does not need a double bond in the reacting molecules (addition polymerisation), but requires two different functional groups on two different molecules.
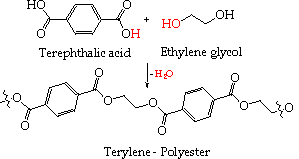
Polyesters
A dicarboxylic acid, such as terephthalic acid, and a diol, such as ethylene glycol, can react with each other at both ends to exclude a molecule of water for each link formed in the polymer chain - producing a polyester.