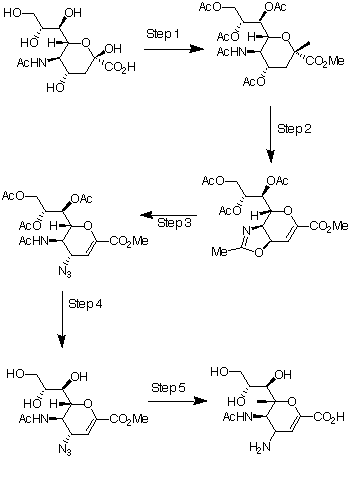
The commercially available
N-acetyl-neuraminic acid 1 is the starting reagent for the most
direct approach to the synthesis of 4-guanidino-Neu5Ac2en (Relenza). In
reaction scheme 113 the steps for
the conversion of N-acetyl-neuraminic acid 1 to its 4-amino
analogue is shown. Step 1 is the addition of methanolic HCl (MeOH and HCl
gas), which produces the methyl ester of 1, followed by acetic
anhydride in pyridine with 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine catalysis, which
produces the penta-acetoxy compound, 2. In step 2, 2 is
converted into the oxazoline 3 at high yield using trimethylsilyl
trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf) in ethyl acetate at 52oC. In
step 3, the azido compound, 4, is produced by the reaction of 3
with trimethylsilyl azide in tert-butyl alcohol at 80oC.
In step 4 catalytic sodium methoxide in methanol was used to remove the
acetate protecting groups from 4 to give triol 5. The
4-amino analogue, 6 was made in step 5, by hydrolysis using
triethylamine in water, hydrogenolysis with a Lindlar catalyst and finally
the addition of Dowex 2 * 8 resin. The triethylamine salt of the 6
was made during hydrogenolysis and the purpose of the Dowex 2 * 8
resin was to desalt this intermediate. The chemical names of the compounds
are:
| 1: N-acetyl-neuraminic acid |
| 2: 5- Acetamido-
3,5- dideoxy- D- glycero- þ- D- galacto- 2- nonulo- pyranosonic
acid methyl ester |
| 3: Methyl (3aR,
4R, 7aR)- 2- Methyl- 4- [(1'S, 2'R)- 1', 2', 3' - triacet- oxypropyl]-
3a, 7a- dihydro- 4H- pyrano [3, 4-d] oxazole- 6- carboxlate. |
| 4: 5- Acetamido-
7, 8, 9- tri- O- acetyl- 2, 6- anhydro- 4- azido- 3, 4, 5- trideoxy-
D- glycero- D- galacto- non- 2- enonic acid methyl
ester. |
| 5: 5- Acetamido-
2, 6- anhydro- 4- azido- 3, 4, 5- trideoxy- D- glycero- D- galacto-
non- 2- enonic acid methyl ester. |
| 6: 5- Acetamido-
4- amino- 2, 6- anhydro- 3, 4, 5- trideoxy- D- glycero- D- galacto-
non- 2- enonic acid. |
|