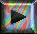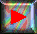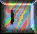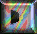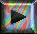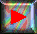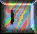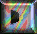 picture of melatonin
(2D) with labelled atoms
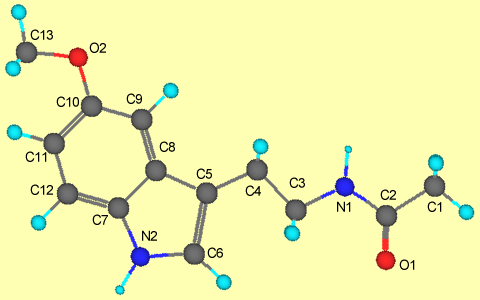
The molecular structure and configuration of melatonin
(N-acetyl- 5 - methoxy tryptamine) can be determined by X-ray diffraction
method. It is crystallized from benzene solution as yellow plates
(m.p. 118-119
oC ), which are shown to be monoxlinic with unit cell parameters
of a= 7.711, b=9.282, c=17.107 Ao and ß =96.77
o from systematic extinctions. The density value of 1.269 g/cc measured
by the flotation method in calsium chloride aqueous solution, indicates
that there are four molecules in a unit cell.
picture of melatonin
(2D) with labelled atoms
The molecular structure and configuration of melatonin
(N-acetyl- 5 - methoxy tryptamine) can be determined by X-ray diffraction
method. It is crystallized from benzene solution as yellow plates
(m.p. 118-119
oC ), which are shown to be monoxlinic with unit cell parameters
of a= 7.711, b=9.282, c=17.107 Ao and ß =96.77
o from systematic extinctions. The density value of 1.269 g/cc measured
by the flotation method in calsium chloride aqueous solution, indicates
that there are four molecules in a unit cell.
The main C-C distance in the benzene ring is 1.402 Ao, while
those of C-C and C-N distances in the pyrrole ring are 1.405 Ao
and 1.394 Ao respectively. The indole part of melatonin
is planar, the average deviation of the atoms from the plane is 0.011 Ao
and the maximum deviation is 0.022 Ao for N(2). C(1),
C(2) and O(1) of acetyl groul and N(1) are almost strictly in a plane.
This plane forms a dihedral angle of 12 o with that of the indole
ring. The atomic parameters and temperature factors (Bij) for
heavy atoms are listed in Table 1 below;
Table 1 : The
atomic parameters and temperature factors (Bij) for heavy atoms
in melatonin molecule
|
Atoms
|
x
|
y
|
z
|
B11
|
B22
|
B33
|
B12
|
B13
|
B23
|
|
C(1)
|
1.1750
|
0.2986
|
0.8350
|
247
|
128
|
29
|
-21
|
-15
|
13
|
|
C(2)
|
1.0969
|
0.3563
|
0.7550
|
205
|
86
|
32
|
3
|
52
|
-8
|
|
C(3)
|
0.9357
|
0.3088
|
0.6258
|
271
|
101
|
20
|
-19
|
-19
|
-3
|
|
C(4)
|
0.8703
|
0.1735
|
0.5814
|
215
|
81
|
25
|
-19
|
-1
|
-1
|
|
C(5)
|
0.8194
|
0.2067
|
0.4943
|
166
|
84
|
28
|
17
|
28
|
1
|
|
C(6)
|
0.8395
|
0.3324
|
0.4541
|
195
|
95
|
31
|
20
|
17
|
14
|
|
C(7)
|
0.7145
|
0.1739
|
0.3648
|
172
|
96
|
28
|
33
|
15
|
2
|
|
C(8)
|
0.7398
|
0.1041
|
0.4383
|
154
|
85
|
25
|
-5
|
24
|
0
|
|
C(9)
|
0.6887
|
-0.0144
|
0.4458
|
165
|
89
|
34
|
-1
|
22
|
-10
|
|
C(10)
|
0.6186
|
-0.1087
|
0.3775
|
182
|
101
|
40
|
-1
|
11
|
-12
|
|
C(11)
|
0.5943
|
-0.0400
|
0.3032
|
186
|
131
|
36
|
16
|
9-
|
-18
|
|
C(12)
|
0.6419
|
0.1030
|
0.2956
|
183
|
138
|
33
|
34
|
12
|
-1
|
|
C(13)
|
0.5866
|
-0.3313
|
0.4485
|
296
|
88
|
55
|
-26
|
22
|
24
|
|
N(1)
|
1.0081
|
0.2636
|
0.7059
|
212
|
79
|
25
|
-12
|
11
|
-7
|
|
N(2)
|
0.7730
|
0.3155
|
0.3754
|
215
|
95
|
36
|
8
|
20
|
11
|
|
O(1)
|
1.1145
|
0.4863
|
0.7368
|
297
|
75
|
33
|
-55
|
29
|
-6
|
|
O(2)
|
0.5659
|
-0.2539
|
0.3756
|
282
|
108
|
52
|
-95
|
7
|
-38
|
-
Bij
are temperature factors ( x 104)
-
Anisotropic temperature factors
are in the form : T= exp[-(B11h2 + B22K2
+ B33l2 + B12hk + B13hl +B23kl)].
-
The average standard deviations
of the coordinations are about 0.007, 0.006 and 0.005 ao for carbon, nitrogen
and oxygen atoms respectively
The torsion angle as defined by Klyne and Prelog (W.
Klyne and V; Prolog, Experientia, 16, 521 (1960) ) is +0.4o
(syn-periplanar) for the atoms C(13)-O(2)-C(10)-C(9), while the equivalent
angle in 5-methoxy-(N,N)-dimethyltryptamine hydrochloride is +2.5o  .
.
Three important torsion angles C(2)-N(1)-C(3)-C(4), N(1)-C(3)-C(4)-C(5)
and C(3)-C(4)-C(6) are +171o (anti-periplanar), -171o
(anti-periplanar) and +6o (syn-periplanar) respectively. The
extended configuration of the side chain attached to C(5) atom is also
found in serotonin-creatinine sulphate complex  .
.
The crystal structure of melatonin reviews that two melatonin molecules
are hydrogen-bonded through N(2)-H----O(1) (2.87 Ao)
into dimer related by centre of symmetry. These dimers are linked together
by N(1)-H----O(1) hydrogen bonds (2.95 Ao ) in the directions
of b and c-axes. The normal van der Waals contacts are found between adjacent
indole rings or methoxy groups to stabilise the crystal structure.