

Preliminary investigations of the addition of ylide-like complexes formed between singlet carbenes and oxygen-containing species to the double bond in ethene have been carried out for the water-methylene and dimethylether-methylene complexes at the RHF/3-21G level. The water-methylene results are in agreement with the previous work of Moreno et al. [5]. In both systems, an intermediate and a transition state have been located; the structures are shown in Figure 6 for H2O-CH2 addition to ethene, and in Figure 7 for CH3OCH3-CH2 addition to ethene.


Figure 6. Optimized geometries at the HF/3-21G level for (a) an intermediate, and (b) the transition state in the addition of H2O-CH2 to ethene.
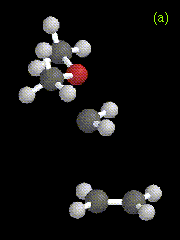
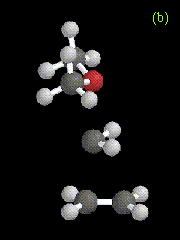
Figure 7. Optimized geometries at the HF/3-21G level for (a) an intermediate, and (b) the transition state in the addition of CH3OCH3-CH2 to ethene.
The structures of the intermediates and transition states obtained for both systems are very similar, and the exothermicity of the reaction is also similar: 72.8 kcal/mol for H2O-CH2 addition, and 72.5 kcal/mol for CH3OCH3-CH2 addition, compared to 93.1 kcal/mol at the RHF/3-21G level for addition of singlet methylene to ethene. The calculated relative energies for reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states are given in Table 4. The energies listed in the Table for each reaction are measured relative to the sum of the energies of separated oxygen-containing species, methylene, and ethene.